Difference between revisions of "Asanga"
From Ingmar de Boer
(→The Life of Asanga: Different Opinions) |
(→List of Gupta Kings) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
==List of Gupta Kings== | ==List of Gupta Kings== | ||
| − | Tāranātha writes in his "History of Buddhism in India" (tr. Lama Chimpa & Alaka Chattopadhyaya, p. 161, see in the Tib. Potala Ed. fol. 57a): | + | [http://www.rigpawiki.org/index.php?title=History_of_Buddhism_in_India Tāranātha] writes in his "History of Buddhism in India" (tr. Lama Chimpa & Alaka Chattopadhyaya, p. 161, see in the Tib. Potala Ed. fol. 57a): |
<ul>"After this, under the patronage of king Gambhīrapakṣa the monks of the four directions assembled in the monastery of U-sma-pu-ri in the city of Sa-ga-ri in the near-west. In this assembly, ārya Asaṅga delivered many sermons according to the understanding of each." | <ul>"After this, under the patronage of king Gambhīrapakṣa the monks of the four directions assembled in the monastery of U-sma-pu-ri in the city of Sa-ga-ri in the near-west. In this assembly, ārya Asaṅga delivered many sermons according to the understanding of each." | ||
Revision as of 01:50, 30 March 2017
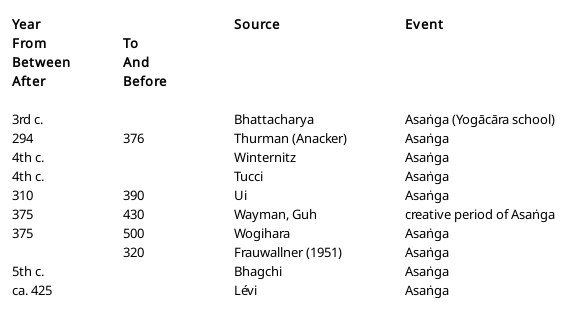
Table
The Life of Asanga: Various Opinions
List of Gupta Kings
Tāranātha writes in his "History of Buddhism in India" (tr. Lama Chimpa & Alaka Chattopadhyaya, p. 161, see in the Tib. Potala Ed. fol. 57a):
- "After this, under the patronage of king Gambhīrapakṣa the monks of the four directions assembled in the monastery of U-sma-pu-ri in the city of Sa-ga-ri in the near-west. In this assembly, ārya Asaṅga delivered many sermons according to the understanding of each."
There are a few more locations where Tāranātha connects the Gupta kings with events in the life of Asaṅga, but if, for simplicity, we only take this one into account, we may derive that Asaṅga was an adult during the reign of Gambhīrapakṣa. The latter was also called Kumāragupta III, who has been in power from around 530 to around 540 CE. From this, we may derive that Asaṅga should have been born some time in the 5th century CE.